A GUIDE FOR FINANCIAL FRAUD INVESTIGATION & PRECAUTION, SHIVANI SHARMA [read my book txt] 📗

- Author: SHIVANI SHARMA
Book online «A GUIDE FOR FINANCIAL FRAUD INVESTIGATION & PRECAUTION, SHIVANI SHARMA [read my book txt] 📗». Author SHIVANI SHARMA
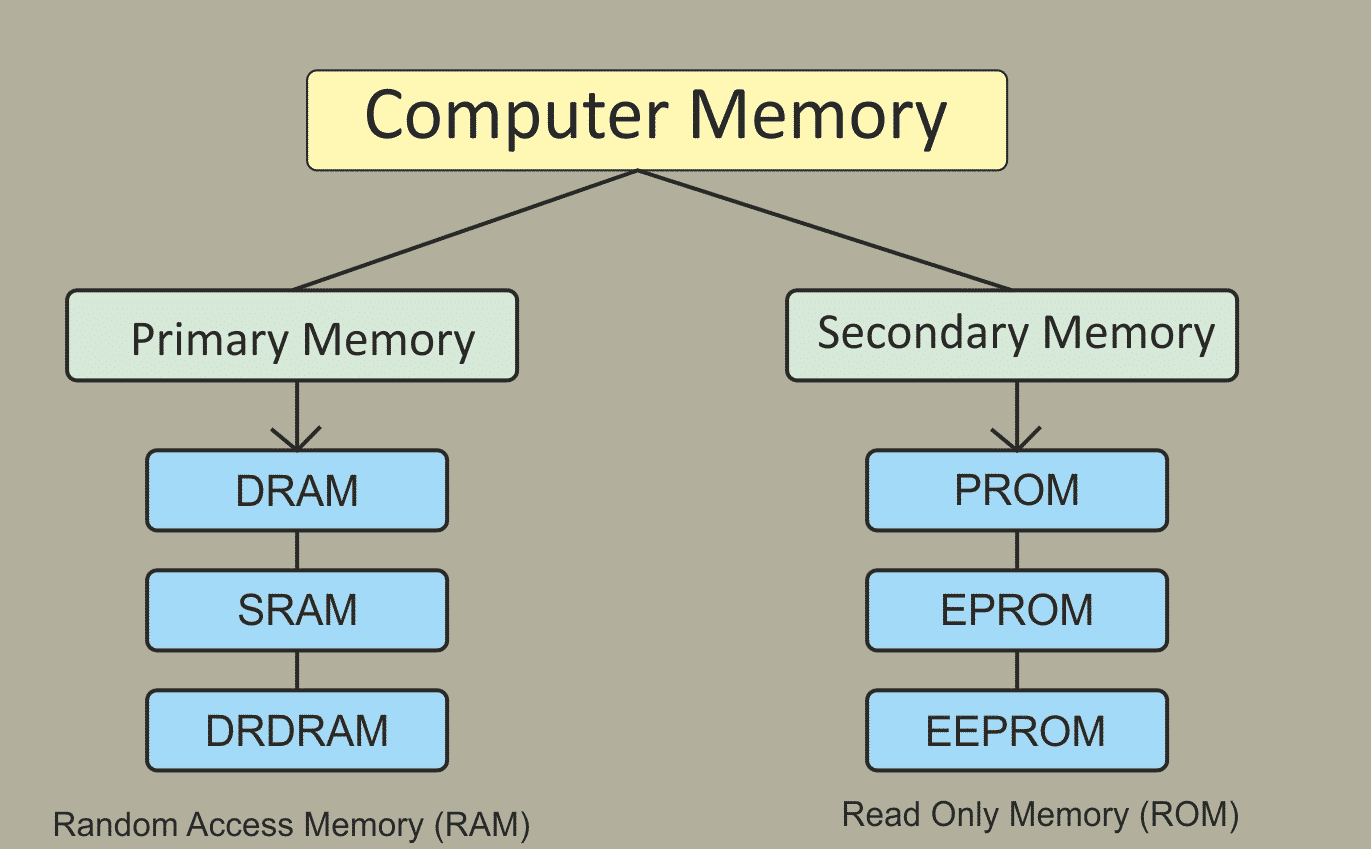
Memory is of three types
Cache Memory Primary Memory Secondary MemoryCache Memory
Cache memory is a very high-speed semiconductor memory which can speed up CPU. It acts as a buffer between the CPU and main memory.
Primary Memory (Main Memory)
Primary memory holds only those data and instructions on which computer is currently working. It has limited capacity and data is lost when power is switched off. It is generally made up of the semiconductor device. The data and instruction require being processed reside in main memory.There are two sub-categories ROM and RAM in Primary memory.
RAM :
The RAM (random access memory) is the place in a computer where the operating system, application programs, and data in current use are kept.
RAM is much faster to read from and write to than the other kinds of storage in a computer, the hard disk, floppy disk, and CD-ROM.
It has two parts:
A. SRAM: Static Random Access Memory
B. DRAM: Dynamic Random Access Memory.
ROM:
As the name suggests ROM, stores information that can only be read. Modifying it is impossible or very difficult.
ROM is also a type of non-volatile storage, which means that the information in it stays even if the computer loses power.
This is another type of ROM that is impossible or difficult to change.
PROM – Programmable Read Only Memory. EPROM – Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory. EEPROM – Electrically Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory.Important Computer Knowledge – Development of computer
Abacus
Abacus is known to be the first mechanical calculating device. Which was used to be performed addition and subtraction easily and speedily. Abacus is made up of the wooden frame in which rod where fitted across with rounds beads sliding on the rod.Pascal Calculator
In the year 1642, Blaise Pascal a French scientist invented the adding machine called Pascal’s calculator, which represents the position of the digit with the help of gears in it.Analytical Engine
A scientist from England knows to be Charles Babbage invented such the machine. This device is known as Analytical engine and it is the first mechanical computer. It includes such feature which we use in today’s computer language. For this great invention of the computer, Sir Charles Babbage is also known as the father of the computer.Generation of computers – Computer Knowledge
Ist Generation: (1940-1956)
Vacuum tubes got use in circuits. These computers are very large in size. It requires a large amount of electricity. They produce more heat. They are less revival. Ex.: ENIAC, UNIVAC.IInd Generation: (1957-1962)
Vacuum tubes got the replacement by transistors in circuits. Small size as compared to Ist Generation computers. Less amount of heat Generation. Less electricity consumption. Ex.: IBM 350IIIrd Generation: (1963-1972)
Transistors got the replacement by I.C. in circuits. (I.C.- Integrated circuits) Small size as compared to IInd Generation computer. Less amount of heat as compared to IInd Generation computer. Less electricity consumption. Faster and more accurate than the IInd Generation computer. Ex.: IBM 360/370IVth Generation: (1973-Present)
LSI and LSVI technologies are used. LSI- Large-scale integration. LSVI-Very large scale integration. Apple-II, STAR 1000Vth Generation: (Present & Beyond)
It is based on the technique of Artificial Intelligence (AI). The computer can understand spoken words. Scientists are constantly working to increase the processing power of computers. They are trying to create a computer with real IQ with the help of advanced programming and technologies. Ex.: IBM Watson.Basic Computer Knowledge – Classification of ComputersClassification of working system
Digital computer
The digital computer is the most common type of computer and is used to process information with quantities using digits, usually using the binary number system. Ex – MacBook.Analog Computer
Analog computer that operates with numbers represented by directly measurable quantities (as voltages or rotations) — compare digital computer, hybrid computer.Hybrid Computer
Hybrid Computer is a computer that combines the characteristics of a digital computer and an analogue computer by its capacity to accept input and provide output in either digital or analogue form and to process information digitally.Software – Computer Knowledge
Computer software is a program or simply software is a series of instructions that directs a computer to perform specific tasks or operations. Computer software consists of computer programs, libraries and related non-executable data (such as online documentation or digital media).
There are two main types of software: systems software and application software.
Systems Software
Systems software includes the programs that dedicate to managing the computer itself, such as the operating system, file management utilities, and disk operating system (or DOS). The operating system manages the computer hardware resources in addition to applications and data. Without systems software installed on our computers, we would have to type the instructions for everything we wanted the computer to do.Applications Software
Application software, or simply applications, are often called productivity programs or end-user programs. They will enable the user to complete tasks such as creating documents, spreadsheets, databases, and publications, doing online research, sending email, designing graphics, running businesses, and even playing games. Application software is specific to the task which can be as simple as a calculator application or as complex as a word processing application. When you begin creating a document, the word processing software has already set the margins, font style and size, and the line spacing for you. But you can change these settings, and you have many more formatting options available. For example, the word processor application makes it easy to add colour, headings, add pictures or delete, copy, move, and change the document’s appearance to suit your needs.Bug
A software bug is an error, flaw, failure or fault in a computer program or system that causes it to produce an incorrect or unexpected result, or to behave in unintended ways.
Virus

Think of a biological virus – the kind that makes you sick. It’s persistently nasty, restricts you from functioning normally and often requires something powerful to get rid of it.
A computer virus is very similar. Designed to relentlessly replicate, computer viruses infect your programs and files, alter the way your computer operates or stop it from working altogether.
How does a computer get a virus?
Even if you’re careful you can pick up computer viruses through normal Web activities like:
Sharing music, files or photos with other users Visiting an infected Website. Opening spam email or an email attachment Downloading free games, toolbars, media players and other system utilities Installing mainstream software applications without fully reading license agreements List of all computer short cut keysList of basic computer shortcut keys:
Alt + F--File menu options in the current program. Alt + E--Edits options in the current program. F1--Universal help (for any sort of program). Ctrl + A--Selects all text. Ctrl + X--Cuts the selected item. Ctrl + Del--Cut selected item. Ctrl + C--Copy the selected item. Ctrl + Ins-- Copy the selected item. Ctrl + V--Paste the selected item. Shift + Ins -- Paste the selected item. Home -- Takes the user to the beginning of the current line. Ctrl + Home--Go to the beginning of the document. End -- Go to the end of the current line. Ctrl + End -- Go to the end of a document. Shift + Home -- Highlight from current position to beginning of the line. Shift + End -- Highlight from current position to end of the line. Ctrl + (Left arrow) -- Move one word to the left at a time. Ctrl + (Right arrow) -- Move one word to the right at a time.
Microsoft Windows shortcut keys list
Alt + Tab -- Switch between open applications. Alt + Shift + Tab -- Switch backward between open applications. Alt + Print Screen -- Create screenshot for the current program. Ctrl + Alt + Del -- Reboot/Windows task manager. Ctrl + Esc -- Bring up the start menu. Alt + Esc -- Switch between applications on the taskbar. F2 -- Rename selected icon. F3 -- Start find from the desktop. F4 -- Open the drive selection when browsing. F5 -- Refresh contents. Alt + F4 -- Close current open program. Ctrl + F4 -- Close window in program. Ctrl + Plus Key-- Automatically adjust widths of all columns in Windows Explorer. Alt + Enter -- Open properties window of selected icon or program. Shift + F10 -- Simulate right-click on selected item. Shift + Del -- Delete programs/files permanently. Holding Shift During Boot up -- Boot safe mode or bypass system files. Holding Shift During Boot up -- When putting in an audio CD, will prevent CD Player from playing.
Word shortcut keys
Ctrl + A -- Select all contents of the page. Ctrl + B -- Bold highlighted selection. Ctrl + C -- Copy selected text. Ctrl + X -- Cut selected text. Ctrl + N -- Open new/blank document. Ctrl + O -- Open options. Ctrl + P -- Open the print window. Ctrl + F -- Open find box. Ctrl + I -- Italicise highlighted selection. Ctrl + K -- Insert link. Ctrl + U -- Underline highlighted selection. Ctrl + V -- Paste. Ctrl + Y -- Redo the last action performed. Ctrl + Z -- Undo last action. Ctrl + G -- Find and replace options. Ctrl + H -- Find and replace options. Ctrl + J -- Justify paragraph alignment. Ctrl + L -- Align selected text or line to the left. Ctrl + Q -- Align selected paragraph to the left. Ctrl + E -- Align selected text or line to the center. Ctrl + R -- Align selected text or line to the right. Ctrl + M -- Indent the paragraph. Ctrl + T -- Hanging indent. Ctrl + D -- Font options. Ctrl + Shift + F -- Change the font. Ctrl + Shift + > -- Increase selected font +1. Ctrl + ] -- Increase selected font +1. Ctrl + [ -- Decrease selected font -1. Ctrl + Shift + * -- View or hide non printing characters. Ctrl + (Left arrow) -- Move one word to the left. Ctrl + (Right arrow) -- Move one word to the right. Ctrl + (Up arrow) -- Move to the beginning of the line or paragraph. Ctrl + (Down arrow) -- Move to the end of the paragraph. Ctrl + Del -- Delete word to the right of the cursor. Ctrl + Backspace -- Delete word to the left of the cursor. Ctrl + End -- Move cursor to end of the document. Ctrl + Home -- Move cursor to the beginning of the document. Ctrl + Space -- Reset highlighted text to default font. Ctrl + 1 -- Single-space lines. Ctrl + 2 -- Double-space lines. Ctrl + 5 -- 1.5-line spacing. Ctrl + Alt + 1 Change text to heading 1. Ctrl + Alt + 2 Change text to heading 2. Ctrl + Alt + 3 Change text to heading 3. F1 -- Open help. Shift + F3 -- Change case of selected text. Shift + Insert -- Paste. F4 -- Repeat the last action performed (Word 2000+). F7 -- Spell check selected text and/or document. Shift + F7 -- Activate the thesaurus. F12 -- Save as. Ctrl + S -- Save. Shift + F12 -- Save. Alt + Shift + D -- Insert the current date. Alt + Shift + T -- Insert the current time. Ctrl + W -- Close document.
Excel shortcut keys
F2 -- Edit the selected cell. F5 -- Go to a specific cell. F7 -- Spell check selected text and/or document. F11 -- Create chart Ctrl + Shift + ; -- Enter the current time. Ctrl + ; -- Enter the current date Alt + Shift + F1 -- Insert new worksheet. Shift + F3 -- Open the Excel formula window. Shift + F5 -- Bring up the search box Ctrl + A -- Select all contents of a worksheet. Ctrl + B -- Bold highlighted selection. Ctrl + I -- Italicize highlighted selection. Ctrl + C -- Copy selected text. Ctrl + V -- Paste Ctrl + D -- Fill Ctrl + K -- Insert link Ctrl + F -- Open find and replace options. Ctrl + G -- Open





Comments (0)